
How GDPR Compliance Impacts SEO: The Ultimate Guide for Website Owners
Here's a breakdown of the risks for website operators who don't comply with GDPR, including hefty fines, legal risks, negative SEO impacts, and decreased ad revenue.
2024-07-200 minute readWeb
Share
Introduction: The Big Picture of GDPR
What is GDPR?

GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, is the EU's data protection law that came into effect on May 25, 2018. It introduces new rules for collecting, storing, processing, and transferring personal data. GDPR aims to strengthen data protection and respect the rights of individuals, ensuring personal data is handled properly and increasing transparency.
Why is GDPR Important?
GDPR lays the groundwork for privacy protection in the digital age, and its impact extends beyond the EU to businesses worldwide. Companies handling personal data of individuals within the EU must comply with GDPR, even if they are based outside the EU. Violations can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover—whichever is higher. This makes GDPR a critical regulation for businesses, demanding serious attention and compliance.
Purpose of This Article
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for website operators to understand and practically comply with GDPR. We will start by explaining the fundamental concepts and key requirements of GDPR. Then, we'll cover how to ensure compliance with GDPR for popular platforms like Google Adsense and others that many website operators use.
By the end of this article, we hope readers will gain a solid understanding of GDPR and feel confident in establishing compliance.
Background and Scope of GDPR
What is GDPR?
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, is a comprehensive EU regulation focused on protecting personal data across the European Union. It establishes standardized rules for handling personal data, enhancing privacy rights, and ensuring transparency. Specifically, GDPR regulates the collection, storage, processing, and transfer of personal data, detailing how businesses should manage this data to safeguard individuals' rights.
Why GDPR Was Introduced
GDPR was introduced in response to the exponential growth of personal data in the digital age and the associated risks of privacy breaches. The rise of the internet has made data collection and usage easier, leading to vast amounts of data being gathered and used by companies. However, this also increases the risk of data leaks and misuse, threatening individuals' privacy.
Previously, the EU's Data Protection Directive (95/46/EC) allowed for varying implementation across member states, leading to inconsistencies in data protection. GDPR was created to address these issues by establishing a unified data protection standard across the EU, updating regulations to match modern technological advancements.
Scope of GDPR
GDPR has a broad scope, applying to any organization processing personal data of individuals within the EU. "Personal data" includes any information that can identify a person, such as names, addresses, email addresses, IP addresses, cookie data, health information, and financial status.
One notable aspect of GDPR is its applicability to companies outside the EU. Specifically, businesses that process personal data of individuals in the EU, or offer goods or services to them, must comply with GDPR, even if they have no physical presence in the EU. This means that any online service or platform accessed by EU consumers must adhere to GDPR.
Global Reach: GDPR's Application Beyond Europe
GDPR's reach extends beyond geographical boundaries to ensure data protection for EU residents regardless of where their data is processed. GDPR applies in the following scenarios:
Companies Based in the EU: All companies with a physical presence in the EU must comply with GDPR when processing personal data of individuals in the EU.
Companies Processing EU Data: Even companies based outside the EU must comply with GDPR if they process personal data of EU residents. This includes online shops and social media platforms serving EU customers.
Companies Targeting the EU Market: Businesses offering goods or services to the EU market are also subject to GDPR, including those conducting marketing activities targeting EU residents.
As website operations typically have a global reach, including the EU, companies must carefully assess whether they fall under GDPR's scope and take necessary actions to comply.
Summary of GDPR Overview
GDPR is a crucial regulation for personal data protection in the digital age, with a wide-ranging impact. Any organization handling personal data of individuals in the EU must comply with GDPR. This regulation aims to enhance data protection and transparency, requiring businesses to take specific steps to ensure compliance.
Got a clear picture of GDPR? In the next section, we'll dive into the key requirements of GDPR.
Key GDPR Requirements: DPOs and Data Subject Rights

Let's explore the key GDPR requirements from the perspectives of Data Protection Officers (DPOs) and the rights of data subjects (individuals whose data is being processed).
Role of the Data Protection Officer (DPO)
The Data Protection Officer (DPO) plays a crucial role in overseeing and managing data protection under GDPR. Responsibilities include developing data protection policies, conducting training and education, and supervising Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs). While appointing a DPO is mandatory for public authorities and large organizations handling significant amounts of personal data, it is also recommended for other businesses.
Rights of Data Subjects
GDPR enhances the rights of data subjects, guaranteeing the following:
Right of Access Data subjects have the right to know how their personal data is being processed. This includes details on the data’s content, processing purposes, storage duration, and any third parties with whom the data is shared. Organizations are required to respond to access requests promptly and free of charge.
Right to Rectification Data subjects can request corrections to inaccurate or incomplete personal data. Organizations must address rectification requests without delay.
Right to Erasure (Right to be Forgotten) Data subjects have the right to delete their personal data under specific conditions, such as when data is no longer needed or if consent is withdrawn. However, this right is not absolute and may be limited by legal obligations or public interests.
Right to Restrict Processing Data subjects can temporarily limit the processing of their data. This might apply if there is a dispute over data accuracy or if processing is unlawful but data subjects prefer not to have it erased.
Right to Data Portability Data subjects can obtain their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. They also have the right to transfer this data to another controller. This right applies when processing is based on consent or a contract.
Right to Object Data subjects can object to the processing of their personal data based on their specific situation, especially when data is processed for direct marketing purposes. In such cases, objections must be accepted unconditionally.
Privacy by Design and Privacy by Default
GDPR mandates that data protection be integrated from the design stage of systems, a principle known as "Privacy by Design." It also requires that data protection settings be set to the minimum necessary by default, known as "Privacy by Default." This emphasizes that data protection should be embedded into the core design of systems rather than being an afterthought.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) evaluates how new data processing activities or technologies affect personal data protection. DPIAs are required for processing activities that pose high risks and help identify and mitigate potential risks. This process ensures the protection of data subjects' rights and freedoms and allows for proactive risk management.
Data Breach Notification Obligation
GDPR mandates that organizations report personal data breaches, such as leaks or unauthorized access, to supervisory authorities within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach. Data subjects must also be notified promptly when their data is at risk. Notifications must include details about the breach's nature, impact, and the measures taken. This obligation aims to prevent risks to data subjects and encourage quick responses to breaches.
Is Non-Compliance with GDPR a Risk for SEO in Website Management?
GDPR compliance is not currently a direct ranking factor for search engines like Google. However, non-compliance can indirectly affect SEO and overall website performance in several ways:
Potential SEO Risks
- Penalties and Trust Issues
- If a website is found to be in violation of GDPR, it might face significant fines and penalties from regulatory authorities. Google could then mark the site as untrustworthy, leading to manual actions or penalties that affect rankings.
- A publicized GDPR violation can damage a website’s credibility, which might affect how search engines and users perceive the site, potentially leading to lower rankings and reduced traffic.
- User Experience Impact
- Users may avoid sites they perceive as non-compliant with GDPR or other privacy regulations. High bounce rates and low engagement times can negatively impact SEO, as search engines consider user behavior signals when determining rankings.
- Websites with poor user experience due to privacy concerns are likely to see a drop in metrics such as time on site and pages per session, which can influence SEO rankings.
- Reduced Advertising Revenue
- Many advertising partners and sponsors prioritize GDPR compliance. Non-compliance might deter potential advertisers, leading to reduced ad fill rates and lower revenue. This could result in fewer resources available for content creation and site improvements, further impacting SEO.
How Website Operators Can Comply with GDPR
For Google AdSense
If you use Google AdSense, complying with GDPR is straightforward by implementing Google's consent management tools. Here’s a guide on setting up these tools:
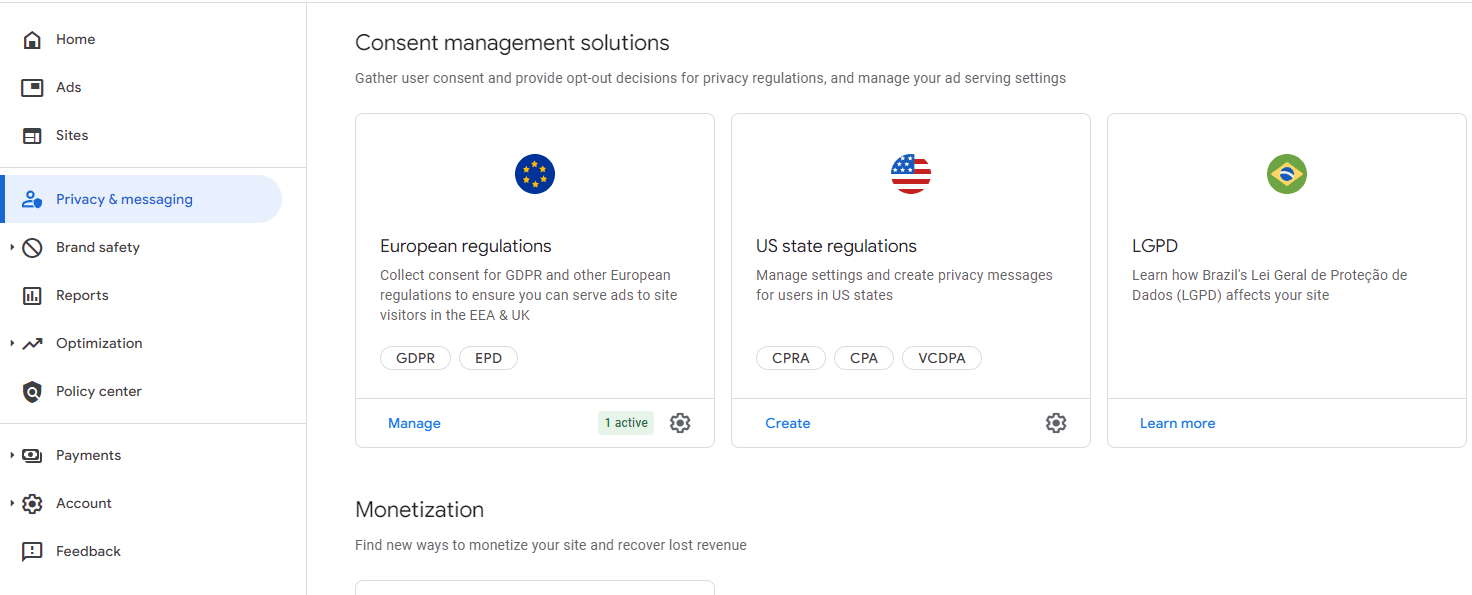
- Access Privacy & Settings
- If you’re already signed up for Google AdSense, go to the Privacy & Settings section in the AdSense management console.
- Implement Google’s Consent Management Tool
- Google provides a free consent management tool that complies with GDPR and other global privacy laws such as the EU’s ePrivacy Directive, CPRA, CPA, VCDPA, and Brazil’s LGPD. Implementing this tool helps manage user consent effectively.
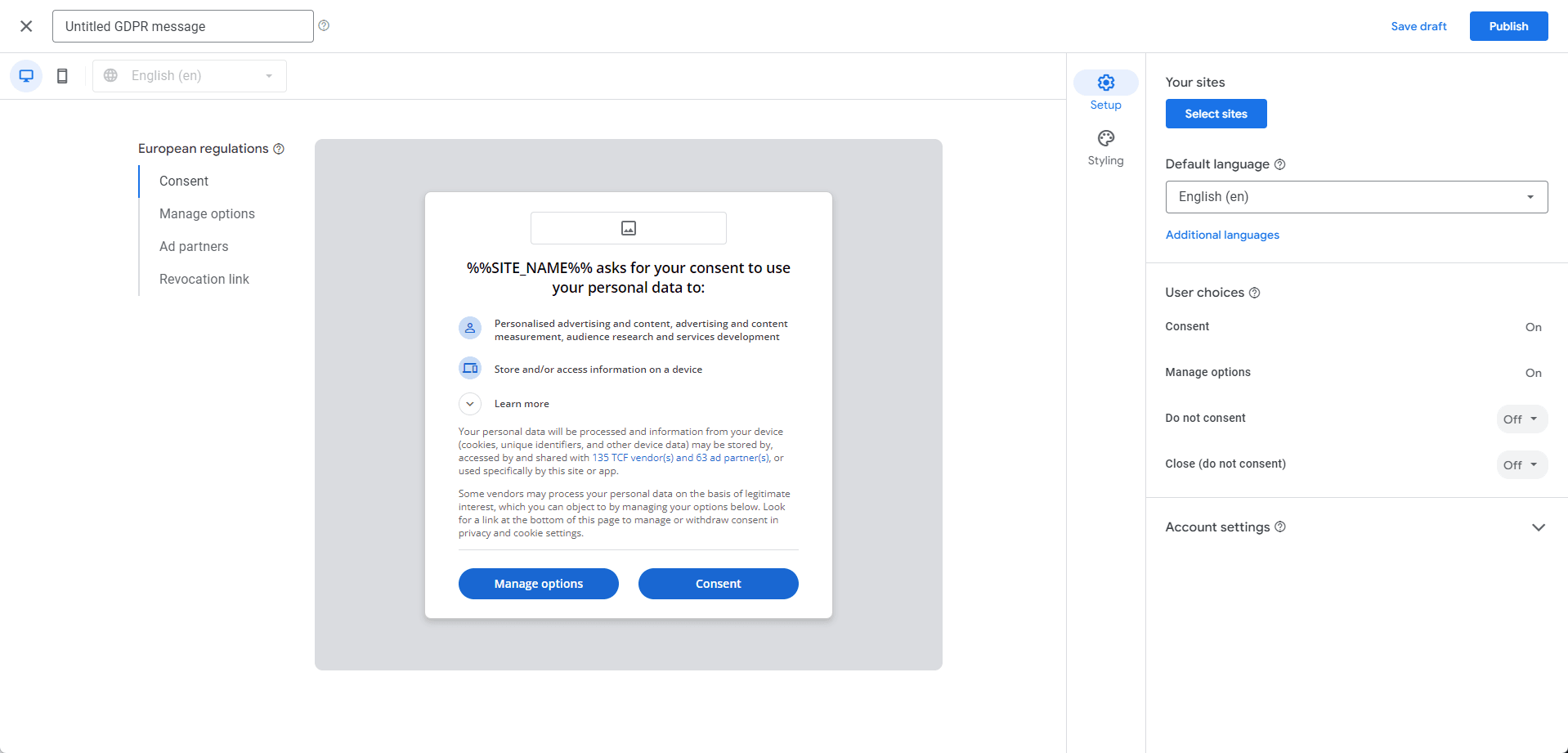
- Configure Consent Options
- Google’s consent management tool allows you to configure how consent messages are displayed and the options available to users. Whether or not to give users the option to refuse consent is up to you, but note that not providing a "Refuse Consent" option could lead to a reduction in ad revenue if users choose not to consent.
- However, in regions where providing a "Refuse Consent" option is legally required, you must comply with these requirements. For example, as of July 2024, data protection authorities in Germany, France (CNIL), Austria (DSB), and Belgium (APD) require that users be given an option to reject cookies.
- No Additional Code Required
- Google’s consent management tool is loaded asynchronously from the Google AdSense code implemented on your website. This means you don’t need to add extra code for implementation, making it very convenient.
Summary
Implementing GDPR compliance through tools like Google’s consent management is not only essential for legal compliance but also helps maintain user trust and avoid potential penalties. It also simplifies the process of managing user consent, ensuring that you adhere to privacy regulations while effectively monetizing your website.
Risks of Non-Compliance
- Legal Risks
- High Fines: GDPR violations can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
- Legal Actions: Data subjects may file lawsuits, leading to substantial legal fees and damages.
- Operational Restrictions: In severe cases, regulatory authorities might order the cessation of data processing activities.
- Reputational Damage: Publicly known breaches can harm your reputation and lead to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
- Operational Risks
- SEO Impact: As discussed, non-compliance can lead to lower search engine rankings due to trust issues and user experience factors.
- User Experience: Poor privacy practices can drive users away, affecting site metrics and engagement.
- Advertising Revenue: Non-compliance might lead to a decrease in ad partnerships, affecting your revenue.
Conclusion
Non-compliance with GDPR poses significant legal and operational risks. Although it may not directly affect SEO at present, the indirect impacts on user trust, engagement, and advertising revenue can influence SEO outcomes over time. Utilizing available consent management tools can help mitigate these risks and ensure compliance, protecting both your site’s reputation and its performance in search engine rankings.